
Net Promoter Score (NPS) is a widely used metric that measures customer loyalty and satisfaction by gauging how likely customers are to recommend your product, service, or company to others.
How NPS works
NPS is calculated based on responses to a single question:
“On a scale of 0 to 10, how likely are you to recommend our product/service/company to a friend or colleague?”
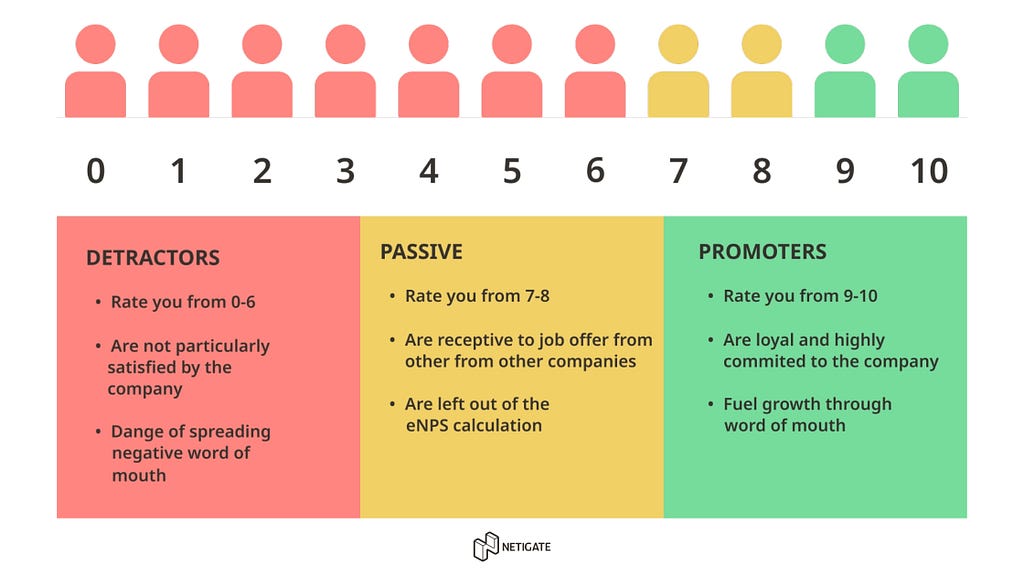
Respondents are then categorized into three groups based on their scores:
- Promoters (9–10): These are loyal users who are likely to refer others, fueling growth through positive word-of-mouth.
- Passives (7–8): These customers are satisfied but not overly enthusiastic. They are vulnerable to competitive offerings.
- Detractors (0–6): These customers are unhappy and could potentially damage your brand through negative word-of-mouth.
Calculating NPS
NPS is calculated using the following formula:
NPS= % of Promoters − % of DetractorsNPS
The result is a score between -100% and +100%
- Positive NPS (>0): Indicates that you have more Promoters than Detractors, which is generally good.
- Negative NPS (<0): Indicates that Detractors outnumber Promoters, which is a sign of customer dissatisfaction and potential churn risk.
When to Use NPS
- Periodic measurement: NPS is typically measured on a regular basis (e.g., quarterly, biannually) to track changes in customer loyalty over time.
- After key milestones: Use NPS after significant customer interactions, such as after a product launch, a major service change, or following customer support interactions.
- Benchmarking agains competitors: NPS is often used to compare performance against industry peers, providing insights into competitive positioning.
9 Tips for making the Most of NPS
1. Ask a follow-up question
Include an open-ended follow-up question like “What is the reason for your score?” to gain qualitative insights. This helps you understand the context and drivers (factors that influence customers’ likelihood to recommend) behind the score, especially for Detractors and Passives.
2. Time the survey
Use automation to send NPS surveys at optimal times. For example, trigger a survey immediately after a purchase or interaction rather than waiting for a scheduled survey period.
3. Segment your analysis
Break down NPS by customer segments (e.g., by demographic, product type, or region) to identify where you’re excelling or falling short. This can reveal specific areas for improvement.
4. Close the loop with detractors
Go beyond the surface-level issues raised by Detractors. Dig deeper to find the root causes and address systemic problems that may be affecting other customers as well.
Engage with Detractors (i.e. conduct interview with them) to understand their concerns and work on resolving them. This can help turn a negative experience into a positive one, potentially converting Detractors into Promoters.
5. Leverage promoters
Encourage Promoters to spread positive word-of-mouth by offering referral programs, testimonials, or incentives. Promoters are your most valuable advocates.
6. Track NPS over time
Monitor your NPS regularly (i.e. once in a quarter) to identify trends. An increasing NPS indicates improving customer loyalty, while a decreasing NPS may signal underlying issues that need attention.
It important to set NPS goals for your product—establish specific NPS targets aligned with broader business objectives. For example, set a goal to improve NPS by a certain percentage to enhance customer retention or to outperform industry benchmarks.
7. Use NPS as a leadership metric
Incorporate NPS into executive dashboards and key performance indicators (KPIs). It provides a clear, easy-to-understand metric that reflects customer sentiment at a high level.
Its also important to link NPS to financial metrics. By correlating NPS with financial metrics such as revenue growth, churn rate, or customer lifetime value (CLTV) you will understand the direct impact of customer loyalty on your bottom line.
8. Benchmark against industry standards
Compare your NPS with industry benchmarks to understand how you stack up against competitors. This can provide context for your score and highlight areas where you need to improve.
9. Combine NPS with other metrics
Use NPS alongside other customer satisfaction metrics like CSAT and CES for a more comprehensive view of customer experience. This can help you understand how loyalty, satisfaction, and ease of use are interconnected.
3 Common Pitfalls to Avoid
1 Overemphasis on the score
Don’t focus solely on the NPS score. The insights from follow-up questions and the actions you take based on feedback are more important.
2. Ignoring passives
While they don’t actively promote or detract, Passives can easily become Detractors if not nurtured. Pay attention to their feedback and work to convert them into Promoters.
3. One-time use
NPS is most valuable when tracked over time. Using it as a one-time measure won’t provide insights into trends or the impact of changes you make.
Want To Learn UX?
Try Interaction Design Foundation. It offers online design courses that cover the entire spectrum of UX design, from foundational to advanced level.
This post contains affiliate link(s)
Net Promoter Score (NPS): Essential Guide was originally published in UX Planet on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.