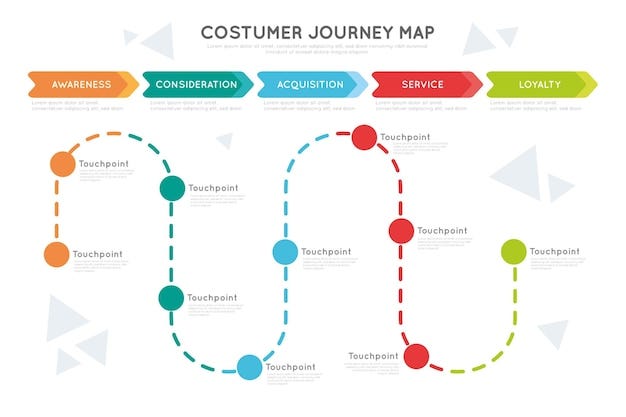
In this article you are going to know below points on User Journey Map
1. Where to do user journey map in the UX process ?
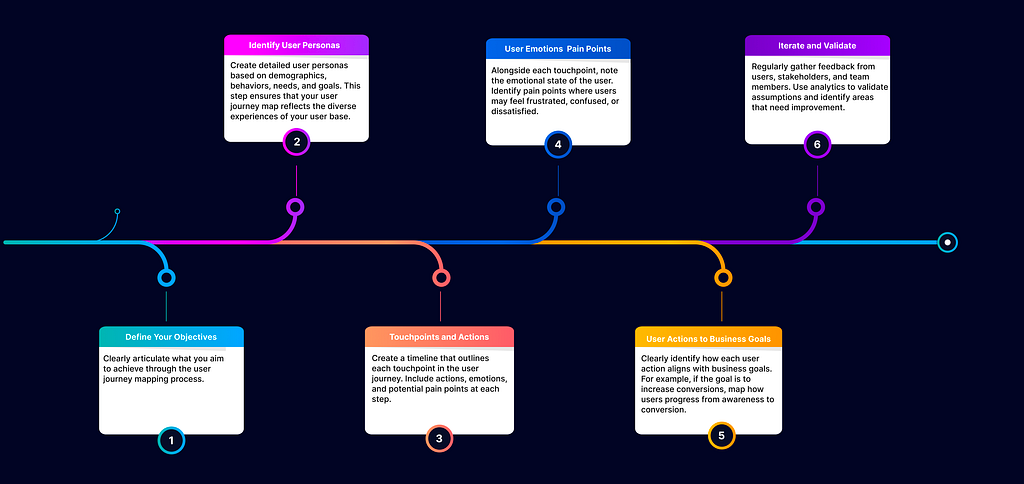
2. What are the steps to create a User journey map ?
3. Type of user journey maps
4. Components of User Journey map
5. Journey Map with Real Project example
6. Benefits
1. Where to do user journey map in UX process
Discovery and Research Phase:
- Objective: Understand user needs, pain points, and behaviors.
- User Journey Map Role: Initial user journey maps can be created to outline existing user experiences and identify areas that need improvement.
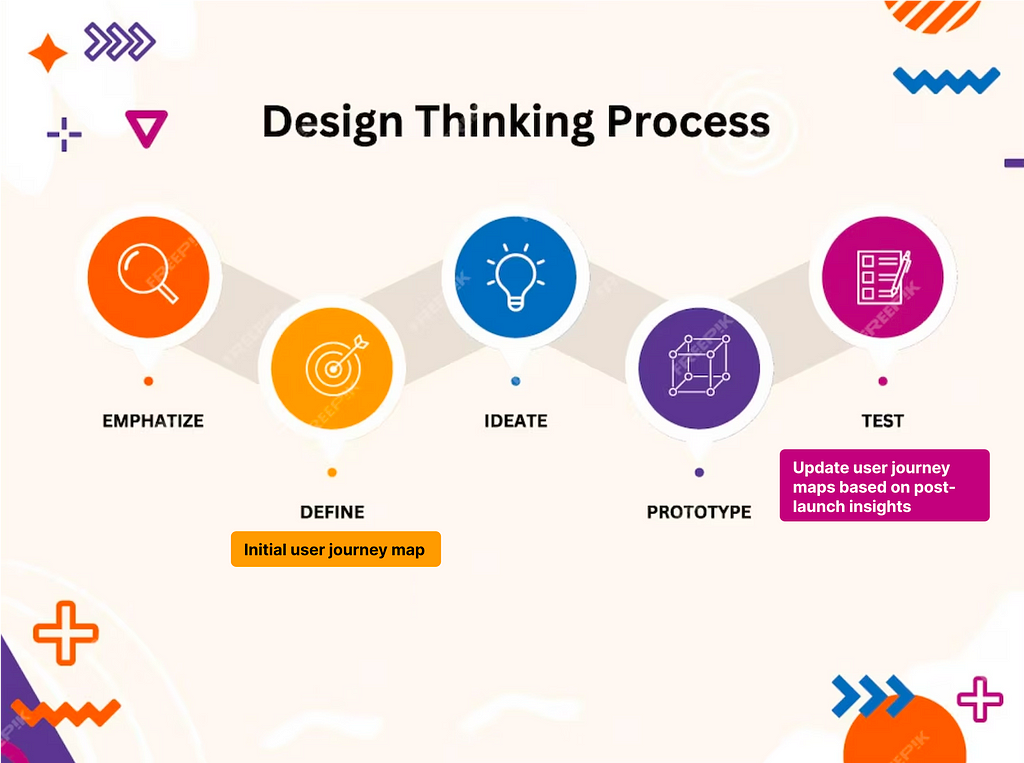
Launch and Post-Launch Evaluation:
- Objective: Release the product and gather user feedback.
- User Journey Map Role: Update user journey maps based on post-launch insights, identifying any areas that may need further refinement.
2. What are the steps to create User journey map ?
3. Type of user journey maps
- Current-State User Journey Map:
Purpose: Illustrates the existing user experience from awareness to post-purchase.
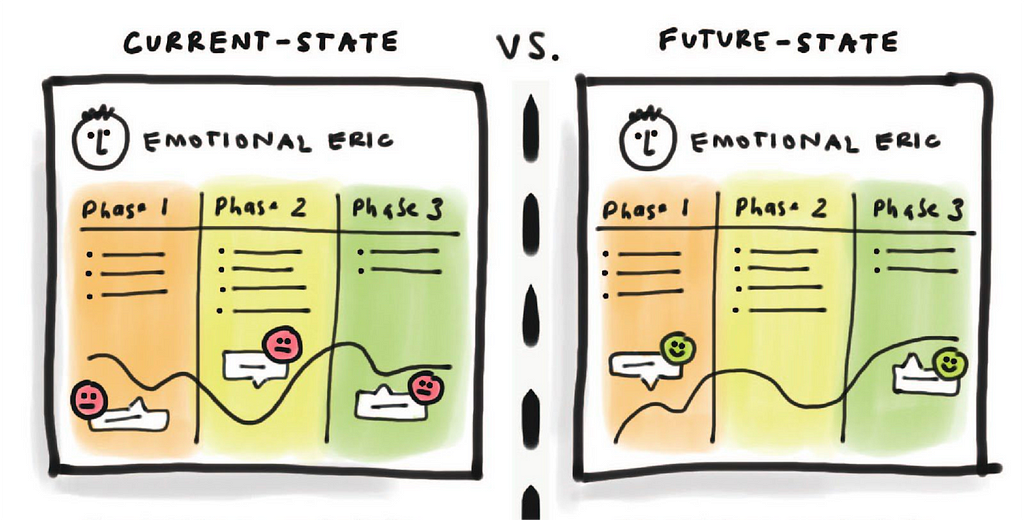
2. Future-State User Journey Map:
Purpose: Envisions an ideal or improved user experience based on desired changes.
3. Persona-Based User Journey Map:
Purpose: Tailored to a specific user persona, detailing their unique needs and pain points.

4. Day in the Life User Journey Map:
Purpose: Captures a user’s experiences throughout an entire day
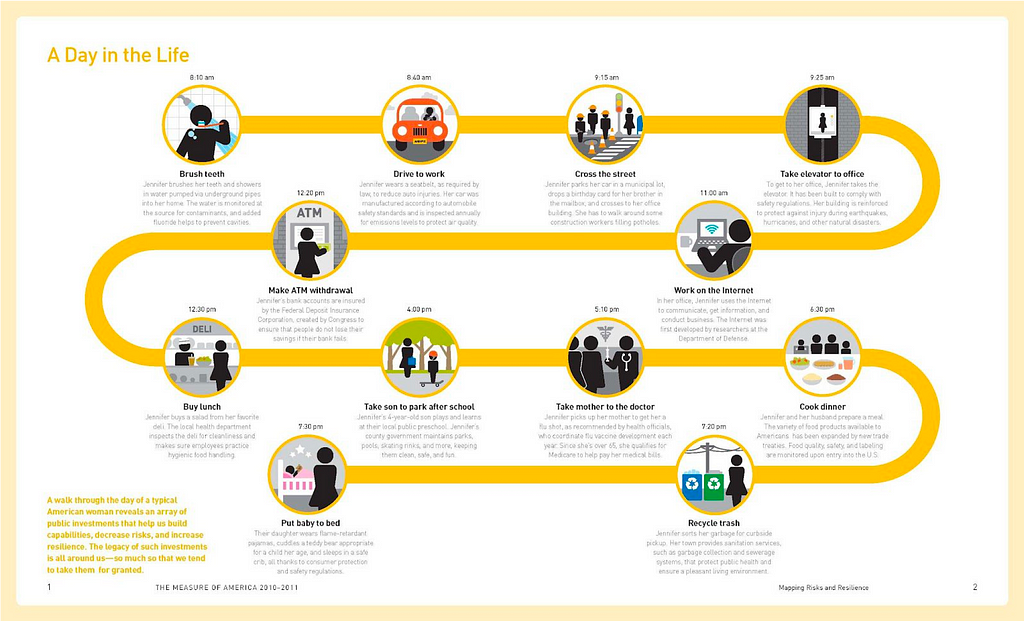
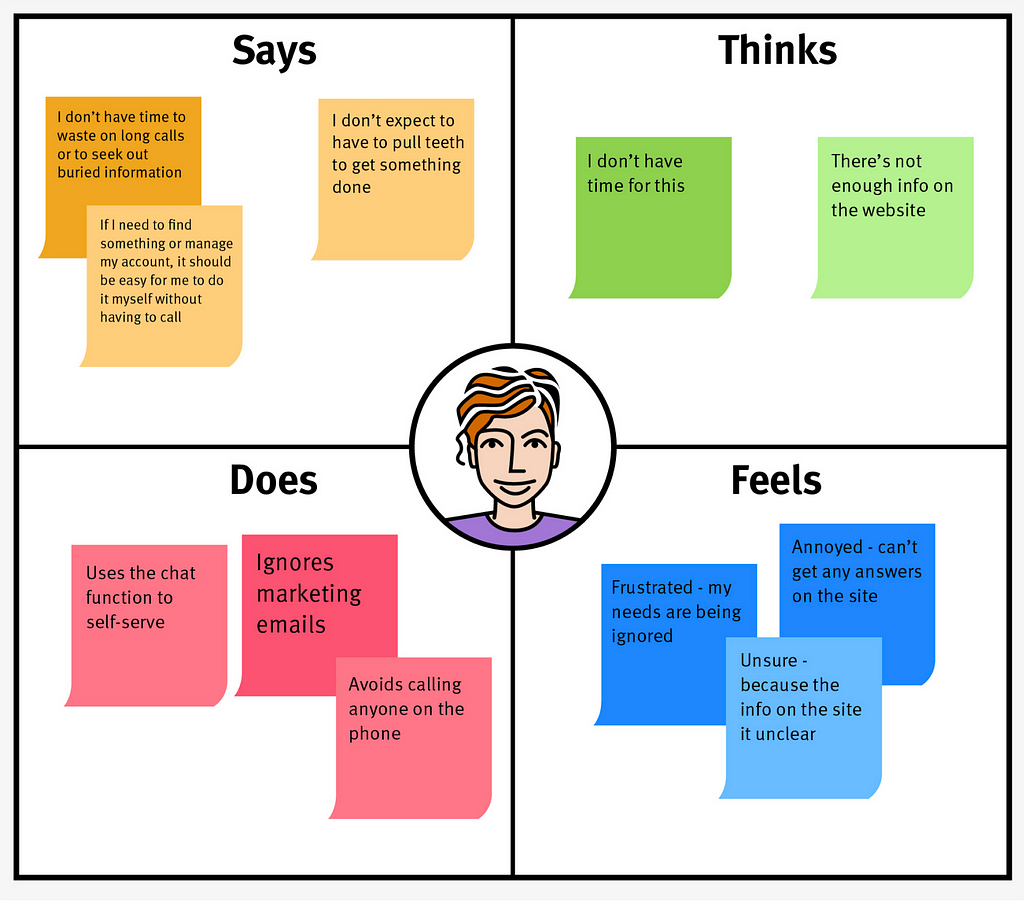
5. Empathy Map:
Purpose: Focuses on understanding the user’s thoughts, feelings, and motivations at different touchpoints.
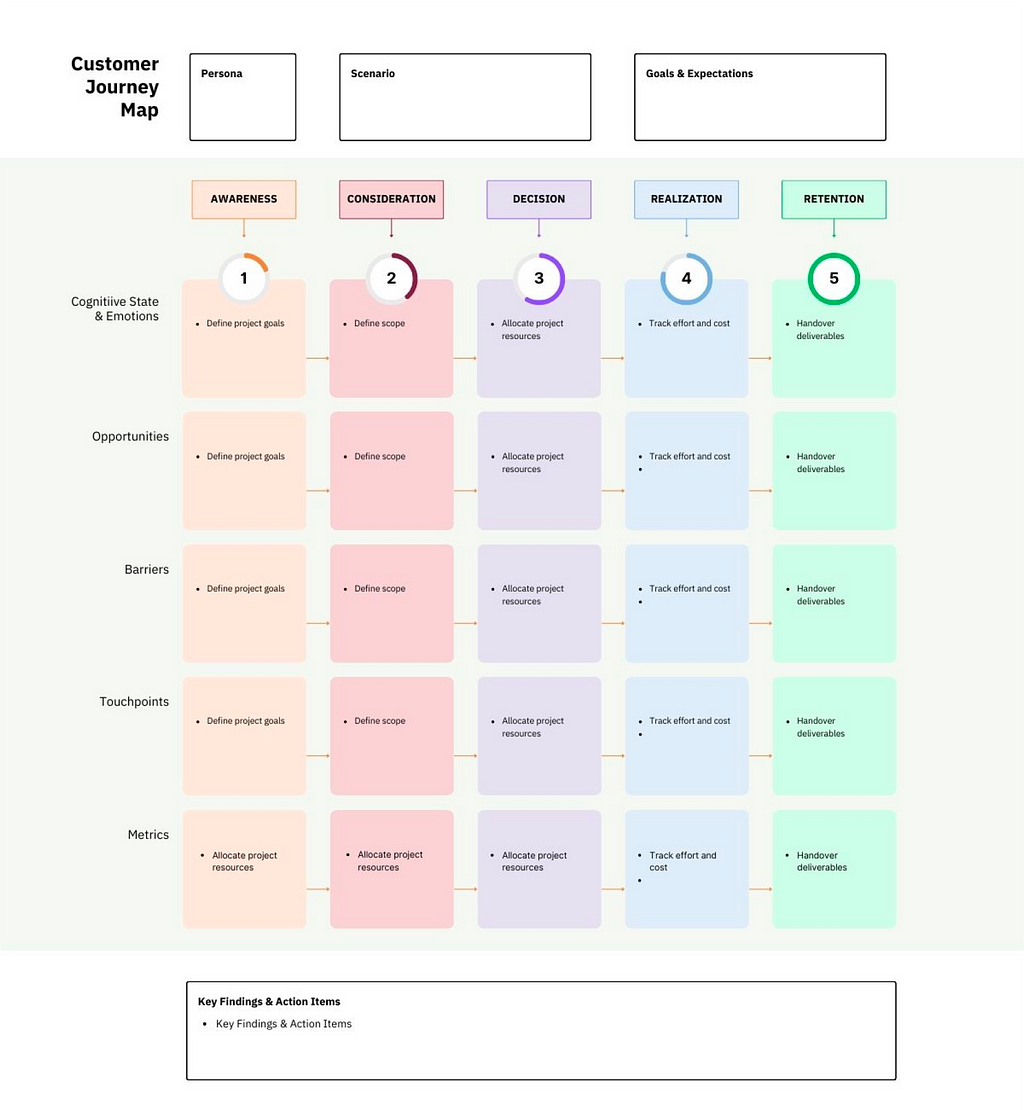
4. Components of a Customer Journey Map
User persona: A clear definition of the user persona(s) that the journey map is designed for.
Stages: A clear breakdown of the stages that the user will go through in their journey, from initial awareness to final action.
Touchpoints: A detailed list of the interactions that the user will have with your product or service throughout their journey.
Emotions: An analysis of the emotions that a user is likely to experience at each stage of the journey.
Painpoints: Identification of the areas of frustration that a user may encounter during their journey.
Opportunities: Calling out opportunities to improve the user experience or add value to the user at each touchpoint.
Metrics: Selection of relevant metrics to track and measure the success of the user journey map.
Visuals: Use of visuals such as icons, graphics, or images to make the user journey map more engaging and easy to understand.
Collaborative input: Collaboration and insight from different teams and stakeholders to ensure alignment and a common understanding of the user journey.
Iterative input: Your user journey map should be an iterative process that is continuously refined and improved based on feedback and new insights
5. Journey Map with Real Project example
Recently, we worked on Dashboard builder project where user can create the dashboard by using widgets (can’t reveal the project name and details as it is confidential). We had discussion with client and user to get the current experience of them.
Below are the key insights/pain points that we found in the research
Key findings/Pain points
- Trying to display too much information on a single dashboard can overwhelm users.
2. Poorly chosen charts or graphs can make it difficult for users to interpret data.
3. Inconsistent use of colors, fonts, and layouts across widgets can create a disjointed user experience.
4. Users may have specific preferences for how they want to view data, and a lack of customization options can be frustrating.
5. Users may find it challenging to navigate or interact with the dashboard.
6. Lack of interactive features can limit the user’s ability to explore data dynamically
Here is the Existing User Journey Map based on the research

We Proposed Below Recommendations/Improvements based on the research
1. Creating user friendly flow for dashboard builder
2.Prioritize key metrics and use progressive disclosure for additional details.
3. Select appropriate data visualization types for different data sets and provide clear labels and legends.
4. Establish a style guide for consistency in design elements throughout the application.
5. Provide users with the ability to customize the layout, colors, and data sources to suit their needs.
6. Prioritize intuitive navigation, provide tooltips, and ensure interactive elements are user-friendly
7. Incorporate features such as drill-downs, filters, and hover effects to enhance interactivity..
8. Design system to maintain the consistency UI
6. Benefits of User Journey Maps
Understanding User Perspectives.
Identifying Touchpoints.
Visualizing User Flows.
Cross-Functional Collaboration.
Spotting Pain Points.
Improving User Engagement.
Aligning with User Goals.
Enhancing User-Centric Design.
Informing Marketing Strategies.
Measuring User Satisfaction.
Predicting User Behavior.
Continuous Improvement.
In essence, user journey maps are powerful tools that provide a holistic view of the user experience, enabling organizations to create more meaningful and effective interactions with their users.
Navigating Success: A Deep Dive into User Journey Maps was originally published in UX Planet on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.