
Agile UX is a design methodology based on the principles of Agile software development. Agile is a proven software development approach that emphasizes flexibility, collaboration and efficiency. Agile UX adopts the same values, reframed in the context of digital design projects. It is a flexible, collaborative, and iterative approach to UX design, focused on delivering high-quality design solutions that consistently meet and exceed the users’ expectations.
Agile UX design teams recognize that user needs and requirements change over time, and they embrace this uncertainty by constantly iterating on their designs and testing them with users. This iterative approach enables them to identify and address potential problems in their designs early on and to deliver products and services that are truly user-centered. It also fosters a culture of collaboration, experimentation and continuous improvement at the workplace.
In this article, we will explore the core fundamentals of the Agile UX design methodology and assess how this design approach helps design teams boost their efficiency and design user-centric digital products and services. We will also provide clear instructions for UX designers who want to adopt this approach to their design process.
What is the Agile UX Process?
Before we discuss Agile UX, let us discuss the design methodology that was prevalent before this iterative and flexible approach was devised. Before transitioning to Agile, most UX design teams operated under the sequential “Waterfall” model of product development. The “Waterfall” model is a linear product design/development methodology that divides the UX design process into multiple, distinct phases such as user research, wireframing, testing, etc.
These phases are completed sequentially one-after-another, with each phase hinging upon the outputs and results of the previous phase:

Waterfall projects are characterized by their fixed timelines and well-defined requirements. This can be beneficial for UX designers, as it allows them to create clear-cut plans and schedules before they start working on projects. However, this rigidity comes with countless costs. In the real world, user needs, requirements, and expectations evolve constantly. If a UX design team discovers a major problem with their design a little too late in the Waterfall process, they will have to start over from scratch. This can be arduous and expensive.
Plus, under this model, project stakeholders do not get the chance to provide feedback on the design process until the prototype or final design is complete. By the time a product is deployed, it might be too late to make significant design changes. Agile is an iterative methodology that addresses all of these problems. Here is how:
- Sprints: Instead of phases, Agile-based UX design projects are broken down into much smaller, iterative cycles. These cycles are called sprints. Each sprint typically lasts for a few days (3 to 14 days). During each sprint, all members of the design team focus on completing specific sets of tasks.
- Cross-Functional: Agile UX teams are cross-functional. They consist of members from all avenues of the product design process, including product managers, UX designers, front-end developers, back-end developers, Quality Assurance (QA) engineers, etc. These professionals combine their expertise to make each sprint perfect: from the initial product vision to the final product deployment.
- Pre-Sprint Planning: At the beginning of each sprint, the design team meets to plan and schedule the upcoming work. They define the key sprint goals, identify the UX design-related tasks that need to be completed, and review the amount of effort required from each team member for each task. Once the sprint plan/schedule is in place, the team begins executing the tasks.
- Collaboration: Now, the cross-functional nature of the Agile UX team comes to the fore. Everyone works together to complete their specific tasks on time and to a super-high standard. With each sprint, the team puts together the main working pieces of the final product design. These small, working pieces are assessed by all team members and key stakeholders in the project. Based on this feedback, the team keeps making incremental improvements to their designs.
- Continuous Improvement: At the end of each sprint, the team holds retrospective meetings, reflecting on what aspects of their work could be improved. The constant feedback helps the team ensure that their work is meeting the needs and expectations of users and stakeholders. With each sprint, the quality of the design improves. The focus on continuous improvement also helps the team become more efficient and effective over time.
In waterfall UX design, design decisions cannot be finalized until the wireframes and mockups are delivered. In Agile UX design, key development and design decisions are finalized after each sprint, which allows for design ideas to be tested and launched more quickly. When it comes to delivering adaptable, user-centered designs that meet users’ needs in a swift manner, Agile UX is an effective and risk-averse design methodology. Adopting the Agile approach may be complicated for design teams at the start.
But, over time, most teams become more collaborative and start releasing working designs to users in a swift manner. Here is a real-world example of how that happens. Imagine that a design agency is designing a new mobile app for food delivery. Let us see how the team will break down the project into multiple sprints to optimize the design process:
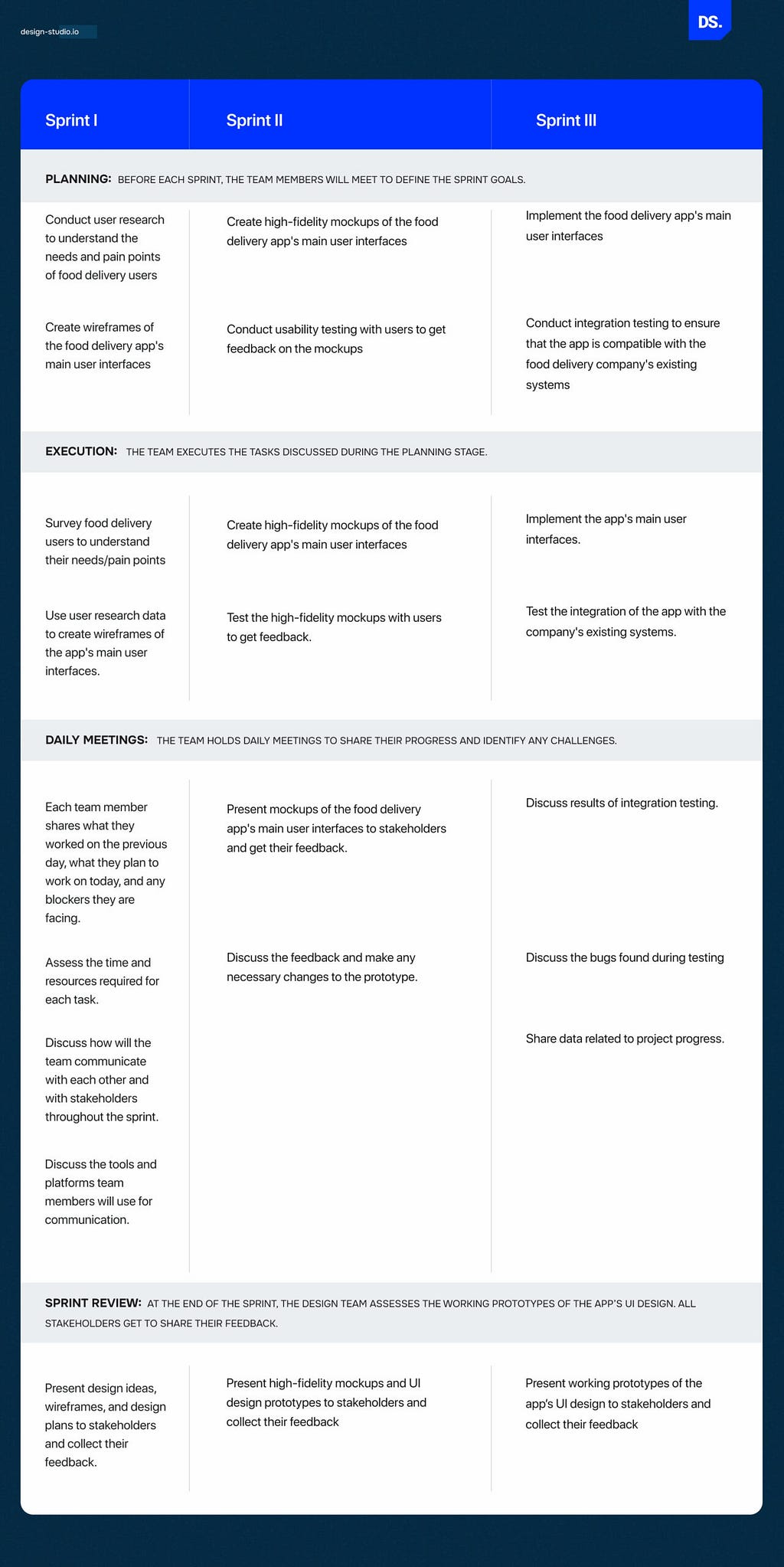
In subsequent sprints, the team can continue to iterate on the app’s design, adding new features/media and fixing bugs. Throughout this process, they can use the feedback from users/stakeholders to identify opportunities for design improvements. Once the design process is complete, the team can deploy it and start monitoring its performance. They can continue to improve the app’s design until it delivers high-quality user experiences.
This was just one example of how apps are designed under the Agile UX model. The specific sprints and tasks that are involved will vary depending on the specific project. However, the approach will be the same: break the project down into short, iterative cycles, use feedback from stakeholders, and be flexible to change throughout the design process. The specific sprints and tasks will also vary depending on the design team’s composition.
Agile UX design teams typically consist of multiple professionals, each with a variety of skills and expertise. From assessing the needs of users to designing the user interface to testing the product, these pros combine their skills to complete each sprint in the most efficient way possible. Here are some of the professionals that are typically found on an Agile UX team:

In addition to these core roles, Agile UX teams may also feature other professionals, such as UX researchers, Quality assurance (QA) engineers, content strategists, visual designers, and more. Before joining the team, these professionals are trained to follow core Agile principles. You can find a comprehensive list of these principles here.
While there are several different ways a team can implement the Agile UX methodology, (Scrum, Lean, Crystal Clear, etc.), the following core Agile principles unify all of these implementation techniques:
- Team collaboration and customer feedback analysis are essential to the design process
- Projects must be completed in increments; the smaller iterations must allow for continuous feedback and improvement throughout the design cycle
- Design decisions must always be driven by user needs, behaviors, and objectives
- All members of the cross-functional team should have a shared understanding of the design goals
- Prototyping and testing should be integral to authorizing design decisions
- Design team members should be open to feedback at every daily meeting
The Need for Agile UX

Ever since its introduction in 2001, the Agile methodology has revolutionized the world of software development. However, its adoption in the world of UX design has been gradual. This is likely due to the decentralized nature of accountability in Agile teams.
In traditional UX design teams, accountability is centralized in the hands of a few team leaders and key stakeholders. In Agile UX teams, accountability rests on the shoulders of each individual team member. This mode of work can be discouraging at first.
But, it swiftly becomes one of the greatest strengths of Agile UX teams. By taking accountability for their individual tasks, UX designers can develop a better understanding of the business goals. Yes, the risk of individual failure is ever-present in Agile teams.
But, these teams have a clear motto when it comes to addressing this risk: “failing early but failing small.” This attitude eliminates complacency and fosters a culture of consistent improvement.
Here are some other notable benefits of adopting the Agile UX design methodology:
- Flexibility: Agile UX projects are non-sequential. They are broken down into small, manageable tasks that can be completed and improved upon during each sprint. It is easy for Agile UX teams to adapt to feedback because they can constantly correct mistakes by adjusting the backlog for the next sprint.
- User-Centricity: Agile UX design is inherently user-centric because team members focus on delivering maximum value to users in each sprint.
- Accountability: Agile UX design is a collaborative process. It requires the active involvement of all team members and everyone is held accountable for the success/failure of design projects.
- Speed: By delivering working designs to users early and on a frequent basis, Agile UX teams can quickly introduce new designs and product features to the market. This speed is critical for obtaining success in today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape.
- Transparency: Team members have no choice but to be 100% transparent about their work because they are asked to share progress updates with stakeholders on a daily basis. This transparency helps build team spirit.
- User Involvement: Agile UX teams involve target users throughout the design process. Their feedback ensures that the designs are meeting key user needs/expectations.
Agile UX Methods: Agile and Lean UX

There are many different methodologies that can be used to efficiently implement Agile UX principles. They include:
- Scrum: A framework for developing/delivering designs in short iterations.
- Kanban: A method for visualizing the design work. Kanban is usually used alongside Scrum to help teams prioritize and stay on track with their work.
- Lean UX: This Agile-based, user-centric approach to UX design focuses on delivering high-value design solutions to users in the shortest possible time periods. To achieve this goal, Lean UX designers conduct tests and experiments on minimum viable product designs (MVP). The results of these tests help UX designers quickly iterate on their designs and validate them with users.
The best method of Agile implementation will obviously depend on the specific needs of the UX design team and the project they are working on. Scrum is the top choice for fast-paced teams that prefer working in short iterations and delivering working designs frequently. Kanban is a good choice for design teams that are highly productive when they get to visualize their work.
Lean UX is focused on minimizing waste and maximizing value. This method is complementary to Agile’s sprint-based model of work which is focused on delivering working designs to users as swiftly and frequently as possible. Lean UX can help Agile UX teams in the following ways:
- Identify the most important user stories
- Create and test design prototypes quickly
- Gather feedback from users early and make appropriate design changes
- Launch design features swiftly and iteratively
These are some of the reasons why the top Agile UX teams adopt many of the core principles of Lean UX.
How to Integrate Agile UX Principles into Your Own Work
Agile is not a one-size-fits-all design methodology. There are at least 10 well-established Agile frameworks that are followed by design teams all across the world. Professional UX designers must master the core fundamentals of Agile and learn about a few of these frameworks. Since Agile UX is somewhat of a departure from the traditional UX design methodologies, this learning process can be difficult for all members of the design team. That is why it is essential for them (product managers, designers, etc.) to take part in professional Agile training sessions.
UI/UX designers must also learn how to think with an Agile mindset. Agile UX teaches us that product design is an incremental process. Hence, designers must embrace feedback and use it to constantly refine their work at every stage of the design process. If you are a business leader, aiming to unleash the power of Agile UX and improve your app or website’s UX quality, contact Design Studio now. We are masters of Agile UX and we cannot wait to help you make the most of this incredible design methodology.
Originally posted on designstudiouiux.com
What is Agile UX? Methods & Process was originally published in UX Planet on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.